2024
Strategic Projects
@Earth Sciences/Geosciences
#nanoparticles
#spICP-ToF-MS
#clustering
#segmentation
Project Summary
The detection and characterization of inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) in natural matrices has relied primarily on single-particle ICP-MS (spICP-MS). In practice, the continuous introduction of an aqueous environmental sample produces element-specific high-frequency time series consisting of background noise randomly interspersed with peaks corresponding to individual NPs. With new generation ICP-ToF-MS, the large amount of data generated poses a challenge for traditional methods to effectively perform NP peak detection. This study proposes a machine learning (ML)-based method for automatic segmentation of spICP-ToF-MS time series using simulated single-channel scenarios with varying parameters to demonstrate its feasibility and robustness.
Mickaël Tharaud
tharaud@ipgp.fr
- Research engineer at IPGP
(specialist in analytical chemistry, with a focus on the detection and characterization of inorganic nanoparticles in aquatic systems thanks to plasma source mass spectrometry)
Jiachen Zhang
Pierre Emmanuel Peyneau
Léonard Seydoux
Projects in the same discipline

Enhancing earthquake location with domain adapation
2023Masters Projects@Earth Sciences and Geosciences +Mathematics/Statistics #Domain adaptation#machine and deep learning#volcano-seismology#earthquake catalogs Project Summaryto be updated. Léonard Seydoux Projects in the same discipline
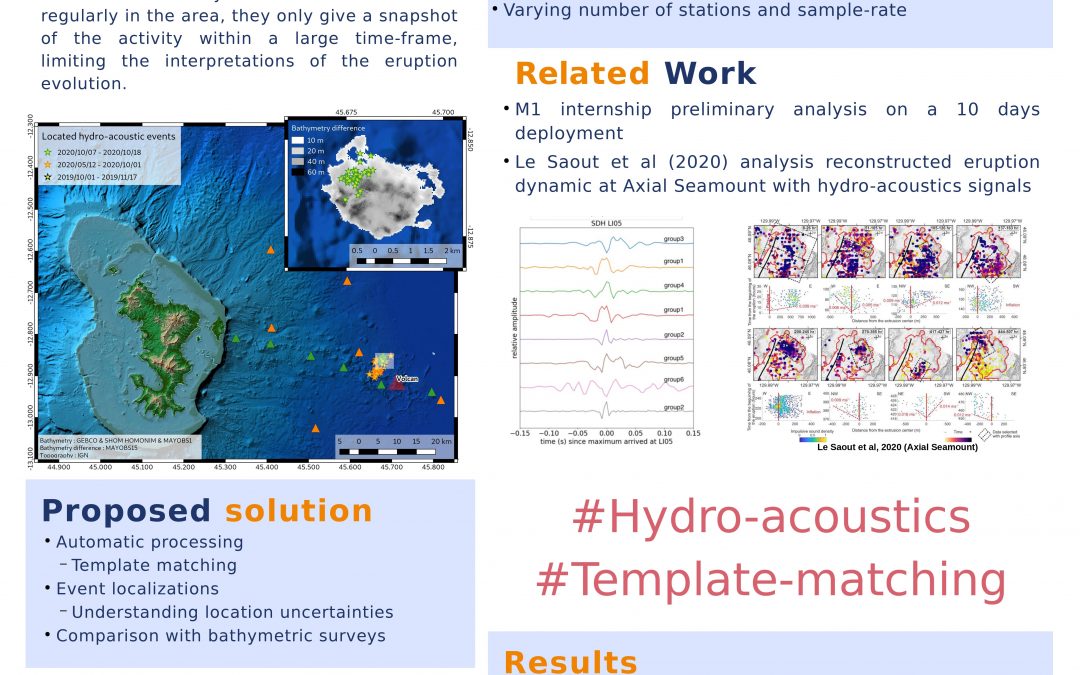
Automatic detection and location of hydro-acoustic signals linked to Mayotte submarine eruption
2022Masters Projects@Earth Sciences and Geosciences +Computer Science+Mathematics/Statistics #Mayotte#hydro-acoustic event#template matching Project SummarySubmarine volcanic eruptions generate numerous seismic and hydro-acoustic signals (West Mata, Axial Seamount)...

Machine learning model of volcanic lava properties helps understanding the dynamics of volcanic eruptions
2021Masters Projects@Earth Sciences and Geosciences +Chemistry #melt#glass#material#properties#neural networks#thermodynamics Project SummaryHow do molten silicate melts move? How do they exchange heat with their surrounding? How do they crystallize? These...

PARKER — Planetary lidAR seeKing for lifE signatuRe
2021Strategic Projects@Earth Sciences and Geosciences +Mathematics/Statistics+Physics/Astronomy #LiDAR#surface of planets#image processing#geomorphology#critical zone#biomass#signal processing#aliasing Project SummaryThe topography of planets bear the imprint of the...
