A Fat Molecule Found to be Critical for Blood Vessel Health

Fats are diverse molecules present throughout the body. Some are beneficial while others become harmful to health if accumulated in the body. In a study conducted by researchers from the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine at the National University of Singapore (NUS), in collaboration with Université Paris Cité and Singapore Lipidomics Incubator (SLING), demonstrated the importance of sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), a fat molecule, in maturing and maintaining healthy blood vessels.
According to the World Health Organization, 15 million people suffer from a stroke each year. Around 13% of these stroke cases are hemorrhagic strokes when weakened blood vessels rupture, which causes brain bleed. The deterioration of vascular integrity and function has also been reported in severe cases of allergic reactions and septic shock. However, current treatments for these medical conditions are not always effective in preventing further complications and mortality.
Fats are diverse molecules which are found throughout the body. Some fat molecules are beneficial, while other fat molecules become detrimental to health if accumulated in the body. One particular fat molecule is sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), which is a potent signaling molecule found in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles, a type of good fat found in the blood. S1P is known to be exported from blood cells and blood vessels into the plasma via transporters. Circulating S1P binds to its receptors (e.g. S1P receptor 1) to regulate several important biological processes.
In this study, researchers at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine) led by Assistant Prof Nguyen Nam Long, in collaboration with Université Paris Cité and Singapore Lipidomics Incubator (SLING), demonstrated that S1P exported from the blood cells and blood vessels play a critical role in maintaining the integrity and functions of the blood vessels.
The team identified Mfsd2b and Spns2 as two proteins responsible for S1P release into blood circulation in early developmental stages of life. When these proteins were eliminated to block S1P export, this resulted in premature death of the embryos due to severe bleeding in the brain as well as in the body.
This reflects the importance of the circulating S1P for the development and maintenance of vascular networks during foetal growth.
In a previous article published in Nature, these researchers uncovered that S1P export from blood cells is essential to prevent allergic shock. In the current study, the team found that S1P export from the cells of the vascular network is also important for blood vessels in coping with vascular stress conditions. These findings reflect the importance of S1P export from blood cells and blood vessels for maintenance of vascular health under disease conditions. The results show the importance of plasma S1P for the development and maturation of blood vessels. Both studies would point to the hypothesis that maintaining blood S1P levels is beneficial for blood vessel-related diseases.
Assistant Professor Nguyen Nam Long, from the Immunology Translational Research Programme (ITRP) and Department of Biochemistry at NUS Medicine, explained, “Blood vessel health is vital for survival. This study reveals important clues that helps us understand the role of S1P in the blood for vascular health and provides exciting avenues for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of a variety of vascular-related diseases and severe allergies.”
The team is looking into studying how the measurements of S1P levels could determine the health of blood vessels in individuals such as COVID-19 patients or develop therapeutics that adjust blood S1P levels. The team is optimistic that this finding could be pivotal in the development of a novel therapeutic strategy to treat allergic conditions and conditions related to the fragility of blood vessels.
Dr Eric Camerer, Inserm Research Director from the Paris Cardiovascular Research Center in Université Paris Cité, added,“S1P is discovered to be essential for the proper development and function of our vascular and immune systems. This study proves that S1P must be actively exported from cells to carry out its vital functions in vascular biology, and has exceeded expectations by identifying the two main transporters responsible for S1P release into circulating fluids.”
Associate Professor Veronique Angeli, director of ITRP added, “This study by Asst Prof Nguyen and our collaborators reflects our commitment towards translational research to further our understanding of the myriad of diseases that continues to grow every day. With every bit of knowledge gained, these discoveries can be translated from bench to bedside to diagnose a wide range of diseases and contribute towards sustainable and preventive care to the populations.”
Source: Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore
Référence
Mfsd2b and Spns2 are essential for maintenance of blood vessels during development and in anaphylactic shock
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111208 (Cell Reports)
For more information, visit https://medicine.nus.edu.sg
Read more

Leiden 2024, UPCité holds France’s top ranking for publication impact
Université Paris Cité maintains its position as the first French university, 16th in Europe and 37th worldwide for its publication impact according to the new Leiden rankings by the Centre for Science and Technology Studies (CWTS). The overall ranking includes 1,506...
read more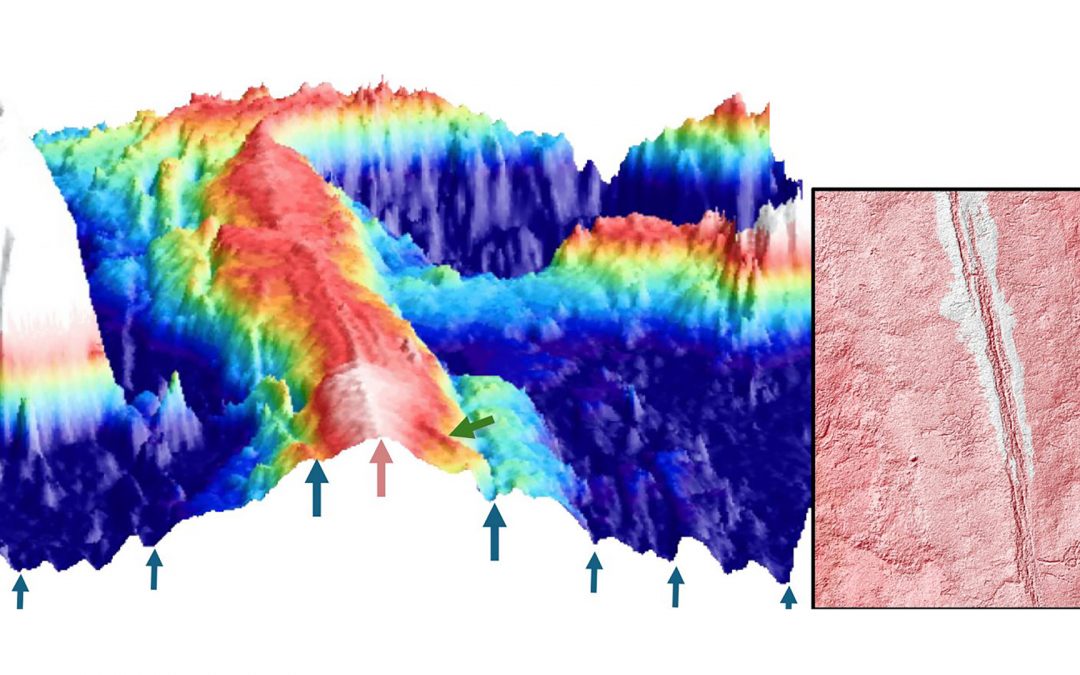
Evidence of magmatically induced faults at the East Pacific Rise
By comparison of ultra-high-resolution 3-D seismic imagery and bathymetry data collected at the East Pacific Rise (EPR) 9º50'N, researchers reveal the existence of magmatic induced faults near the ridge axis.
read more
Convergences: A Strategic Alliance paving the Future of Biology-Health Research
A key milestone for the partnership between Institut Pasteur and Université Paris Cité, the first “Convergences” scientific seminar took place on June 17th at the university’s head office at Odéon.
read more
Université Paris Cité receives 2 grants from Marie Sklodowska Curie Actions programme !
The results of the MSCA Staff Exchange 2023 call for proposals were published on May 28 2024. Université Paris Cité congratulates its two winners, Sylvain Chaty, Professor and Vice President for Culture, Science and Society at the AstroParticle and Cosmology...
read more