Our liver plays a role in regulating our central biological clock, scientists from CNRS and Université Paris have discovered. The results of their study, published on 17 May in Science Advances, show that the biological clock of mice can be reprogrammed by inserting human liver cells into the animal’s liver.
Organisms rely on a biological clock known as the ‘circadian’ clock to regulate their activity according to the time of day. A central clock, constituted by a group of brain cells — the suprachiasmatic nuclei, or SCN — synchronises the circadian clocks present in all body’s organs, called ‘peripheral’ clocks. Until now, synchronisation of the circadian cycle in mammals was thought to be a one-way mechanism in which the suprachiasmatic nuclei alone synchronized the peripheral clocks.
Scientists from CNRS, Université Paris Cité1 and the University of Queensland2 , however, in the framework of a joint EU endeavour3 , have just shown that the liver also influences peripheral clocks. Teams studied a chimeric mouse model with a liver containing human hepatocytes and observed that the daily cycle of these usually nocturnal animals had advanced by two hours.
The mice became active and began feeding two hours before nightfall, thus becoming partly diurnal. The researchers believe this shift comes from the mice’s central clock being taken over by the human liver cells in this chimeric animal model. These cells can thus affect the entire rhythmic physiology of the animals, including the clocks of the peripheral organs.
Findings suggest that a change in liver clock — for example in pathological condition such as cirrhosis — could affect the synchronisation function of the central clock. This in turn could affect the entire circadian physiology, including the sleep/wake cycle, and contribute to the development of metabolic disease. It also suggests that restoring disrupted liver biological rythm could benefit the entire body metabolism. The hormonal and nervous mechanisms driving this dialogue between the brain, liver and biological clock remain to be identified.
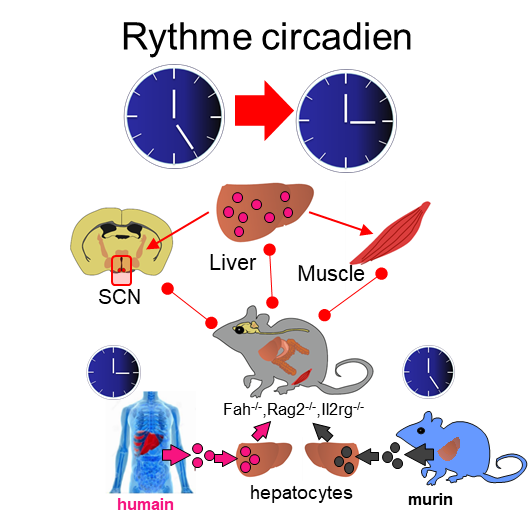
A “humanised” mouse model receives liver cells from healthy mice (control group) or human liver cells (humanised mice). The presence of human liver cells leads to a modification in the circadian clock of the liver and muscle and affects the central clock (the suprachiasmatic nuclei). This results in a phase advance in circadian rhythm in the humanised animal, the metabolism and behaviour of which shifts forward by a few hours.
© Luquet et al./ Science Advances
Notes
- At the Unité biologie fonctionnelle et adaptative (CNRS/INSERM/Université Paris Cité)
- Institute for Molecular Bioscience, The University of Queensland, Australia
- Study carried out as part of the EU-funded HUMAN consortium on Health and the Understanding of Metabolism, Aging and Nutrition.
Mice with humanized livers reveal the role of hepatocyte clocks in rhythmic behavior.
DOI : 10.1126/sciadv.adf2982
Read more
![[Cardiovascular Sciences] “Open UE”: looking back on an interdisciplinary adventure!](https://u-paris.fr/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/Sans-titre-1920-x-1080-px58-1080x675.jpg)
[Cardiovascular Sciences] “Open UE”: looking back on an interdisciplinary adventure!
The “open UE”, launched by the Graduate School Cardiovascular Sciences, brought together researchers, clinicians, and experts from diverse fields for a week to explore major issues in biomedical and translational research. Open to all students across the 29 Graduate Schools of Université Paris Cité, it offered a unique space for learning and interdisciplinary exchange.
read more
Scientific event: the Neuroscience Graduate School highlights its young researchers
The Neuroscience Graduate School held the third edition of its scientific event, giving students from across the Graduate School the opportunity to present their research work. This now-established meeting has become a key moment for bringing together Master’s...
read more
Call for applications for US Visiting Faculty 2026-2027
Committed to supporting research at the highest level through their partnership, Université Paris Cité and Sciences Po are calling for outstanding applications for visiting faculty from the United States. Apply before January 30, 2026.Candidates selected under a...
read more
Université Paris Cité welcomed new international staff members
On November 14th, Université Paris Cité welcomed nearly 50 new international staff members – visiting lecturers, doctoral and post-doctoral students, researchers, and contractual lecturer-researchers of foreign nationality – who have arrived since the beginning of...
read more